Mastering Proper Running Form
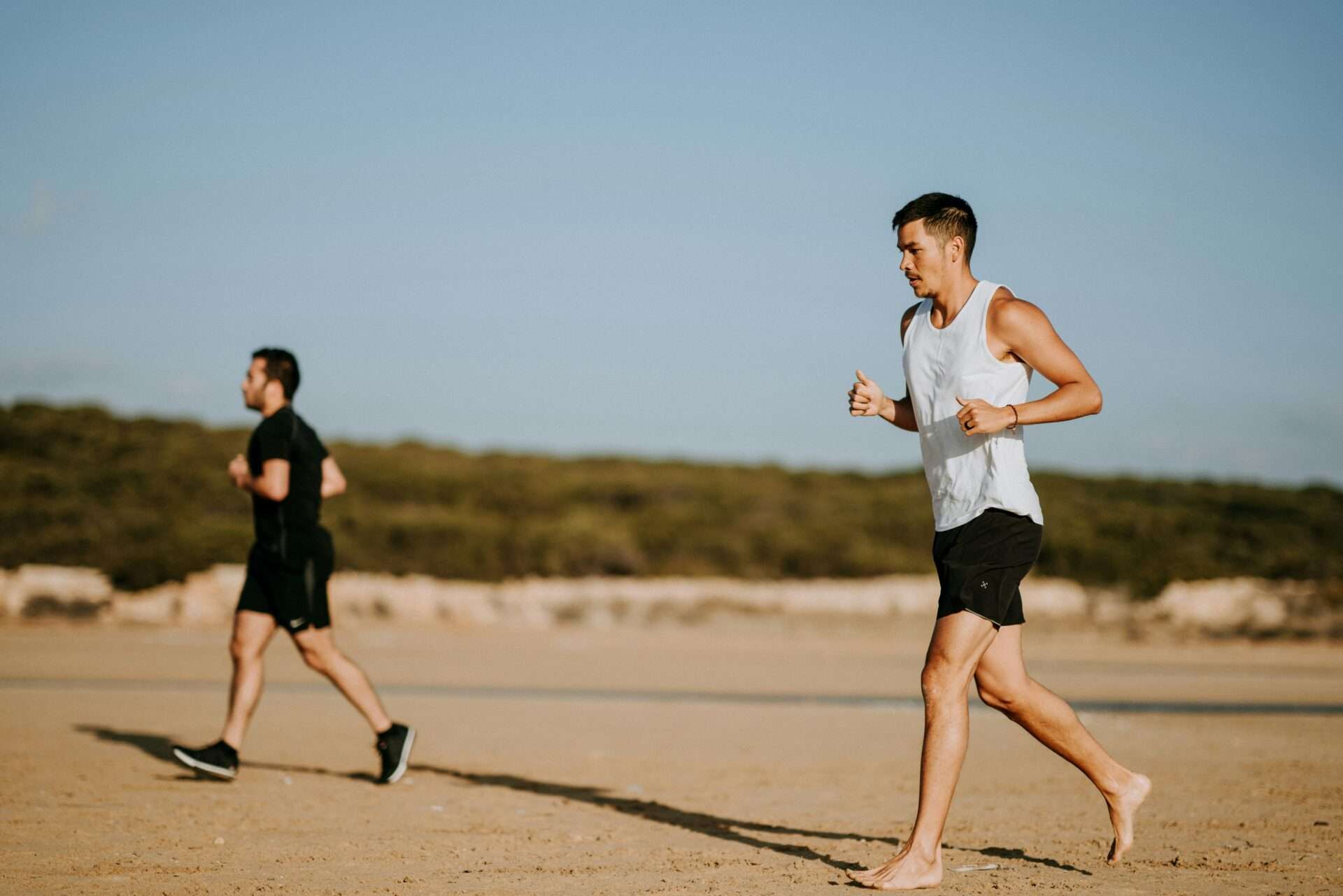
Developing efficient running form is essential for performance enhancement and injury prevention. This guide explores biomechanical principles and practical strategies to help runners of all levels refine their technique.
Core Principles of Efficient Form
- Upright posture with slight forward lean
- Relaxed shoulders and arms
- Midfoot strike pattern
- 180+ steps per minute cadence
Understanding Your Biomechanics
Assessing Your Natural Running Style
Key evaluation methods:
- Video analysis from multiple angles
- Professional gait assessment
- Self-monitoring of comfort and efficiency
Common Form Variations
Normal differences among runners:
- Foot strike patterns (heel/midfoot/forefoot)
- Arm swing width and height
- Stride length and turnover rate
Form Improvement Techniques
Posture Corrections
Essential alignment adjustments:
- Head up, eyes looking 20-30 feet ahead
- Shoulders relaxed and slightly back
- Core engaged to maintain neutral spine
Arm Mechanics
Optimal upper body technique:
- 90-degree elbow bend
- Hands relaxed (imagine holding potato chips)
- Arms swinging forward/back, not across body
Training Tools and Methods
Form Drills
Effective practice exercises:
- High knees (emphasizes knee drive)
- Butt kicks (improves hamstring mobility)
- Strides (short accelerations focusing on form)
Technology Aids
Helpful analysis tools:
- Wearable sensors for cadence tracking
- Smartphone apps for video breakdown
- Treadmill with side/front mirrors
Injury Prevention Strategies
Common Form-Related Injuries
Issuses to watch for:
- Shin splints (overstriding)
- IT band syndrome (cross-body arm swing)
- Plantar fasciitis (heavy heel striking)
Corrective Exercises
Strength and mobility work:
- Single-leg squats (improves stability)
- Hip flexor stretches (enhances range)
- Calf raises (strengthens foot strike)
Professional Guidance
When to Seek Coaching
Consider professional help for:
- Persistent pain or injuries
- Performance plateaus
- Major technique overhauls
Finding the Right Coach
Qualities to look for:
- Certification in running mechanics
- Experience with your running level
- Video analysis capabilities
Form Maintenance
Routine Check-Ins
Periodic self-assessment:
- Monthly video recordings
- Attention to comfort changes
- Monitoring fatigue patterns
Adapting to Changes
When to adjust form:
- After significant weight change
- Following injuries
- With advancing age
Conclusion
Proper running form evolves through consistent practice, self-awareness, and targeted improvements. By focusing on biomechanical efficiency and listening to your body, you can develop a sustainable running style that enhances performance while minimizing injury risk.
Frequently Asked Questions
How long does it take to improve running form?
Most runners see noticeable improvements within 4-6 weeks of focused practice, but permanent changes typically require 3-6 months of consistent effort.
Should I change my foot strike pattern?
Only if your current strike causes pain or inefficiency. Most runners naturally gravitate toward their optimal strike pattern when cadence and posture are correct.
How often should I do form drills?
Incorporate form drills 2-3 times weekly, either as part of your warm-up or as dedicated technique sessions.
Can shoes affect my running form?
Yes, footwear significantly impacts biomechanics. Get properly fitted shoes that complement your natural gait pattern.
Is perfect running form achievable?
There’s no universal “perfect” form, but every runner can develop their most efficient, injury-resistant technique through mindful practice.